29 Cu Copper 63.546. Atomic Number: 29. Atomic Weight: 63.546. Melting Point: 1357.77 K (1084.62°C or 1984.32°F) Boiling Point: 2835 K (2562°C or 4644°F) Density: 8.933 grams per cubic centimeter. Phase at Room Temperature: Solid. Element Classification: Metal. Period Number: 4. Group Number: 11. Group Name: none. What's in a name? Atomic Number of Copper. Copper is a chemical element with atomic number 29 which means there are 29 protons and 29 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Copper is Cu. Atomic Mass of Copper. Atomic mass of Copper is 63.546 u. Atomic Mass 63,546 Learn more about the atomic mass. Sources Pure copper occurs rarely in nature. Usually found in sulfides as in chalcopyrite (CuFeS2), coveline (CuS), chalcosine (Cu2S) or oxides like cuprite (Cu2O). Atomic Number 29 Learn more about the atomic number. Atomic Symbol Cu Name Origin.
The Element Copper
[Click for Isotope Data]
Atomic Number: 29
Atomic Weight: 63.546
Melting Point: 1357.77 K (1084.62°C or 1984.32°F)
Boiling Point: 2835 K (2562°C or 4644°F)
Density: 8.933 grams per cubic centimeter
Phase at Room Temperature: Solid
Element Classification: Metal
Configuring VS Code. Open the Debug panel (CTRL + SHIFT + D) and select “Add Configuration GDB” through the top left dropdown arrow. Create a GDB configuration in launch.json and add the following. Note: Change the paths in “target”, “gdbpath”, and “autorun” to the correct locations. VisualGDB includes a powerful Clang-based IntelliSense engine that fully supports GCC-specific code and is integrated with Make, QMake and CMake. Advanced features include: Easy navigation around your code with CodeJumps; Create implementations for newly added methods; Create-from-use for methods and constructors. Visual Studio Code supports the following debuggers for C/C depending on the operating system you are using: Linux: GDB; macOS: LLDB or GDB; Windows: the Visual Studio Windows Debugger or GDB (using Cygwin or MinGW) Windows debugging with GDB. You can debug Windows applications created using Cygwin or MinGW by using VS Code. Gdb visual studio code. Pick any port you like - here 1234. Test the connection to gdbserver from your local machine by typing. Gdb (gdb) target remote myremotehostname:1234. Trigger any gdb command to check whether it works - e.g. C (or continue) to continue running mybinary. Put the following into your.vscode/launch.json. Using GCC with MinGW. In this tutorial, you configure Visual Studio Code to use the GCC C compiler (g) and GDB debugger from mingw-w64 to create programs that run on Windows. After configuring VS Code, you will compile and debug a simple Hello World program in VS Code. This tutorial does not teach you about GCC, GDB, Mingw-w64, or the C language.
Period Number: 4

Group Number: 11
Group Name: none
What's in a name? From the Latin word cuprum, which means 'from the island of Cyprus.'
Say what? Copper is pronounced as KOP-er.
History and Uses:
Archaeological evidence suggests that people have been using copper for at least 11,000 years. Relatively easy to mine and refine, people discovered methods for extracting copper from its ores at least 7,000 years ago. The Roman Empire obtained most of its copper from the island of Cyprus, which is where copper's name originated. Today, copper is primarily obtained from the ores cuprite (CuO2), tenorite (CuO), malachite (CuO3·Cu(OH)2), chalcocite (Cu2S), covellite (CuS) and bornite (Cu6FeS4). Large deposits of copper ore are located in the United States, Chile, Zambia, Zaire, Peru and Canada.
Used in large amounts by the electrical industry in the form of wire, copper is second only to silver in electrical conductance. Since it resists corrosion from the air, moisture and seawater, copper has been widely used in coins. Although once made nearly entirely from copper, American pennies are now made from zinc that has been coated with copper. Copper is also used to make water pipes and jewelry, as well as other items.
Pure copper is usually too soft for most uses. People first learned about 5,000 years ago that copper can be strengthened if it is mixed with other metals. The two most familiar alloys of copper are bronze and brass. Bronze, the first alloy created by people, is a mix of copper that contains as much as 25% tin. Early people used bronze to make tools, weaponry, containers and ornamental items. Brass, a mix of copper that contains between 5% and 45% zinc, was first used about 2,500 years ago. The Romans were the first to make extensive use of brass, using it to make such things as coins, kettles and ornamental objects. Today, brass is also used in some musical instruments, screws and other hardware that must resist corrosion.
Hydrated copper sulfate (CuSO4·H2O), also known as blue vitriol, is the best known copper compound. It is used as an agricultural poison, as an algicide in water purification and as a blue pigment for inks. Cuperic chloride (CuCl2), another copper compound, is used to fix dyes to fabrics. Cuprous chloride (CuCl) is a poisonous white powder that is chiefly used to absorb carbon dioxide (CO2). Copper cyanide (CuCN) is commonly used in electroplating.
Estimated Crustal Abundance: 6.0×101 milligrams per kilogram

Estimated Oceanic Abundance: 2.5×10-4 milligrams per liter
Cu Element Atomic Number
Number of Stable Isotopes: 2 (View all isotope data)
Ionization Energy: 7.726 eV
Oxidation States: +2, +1
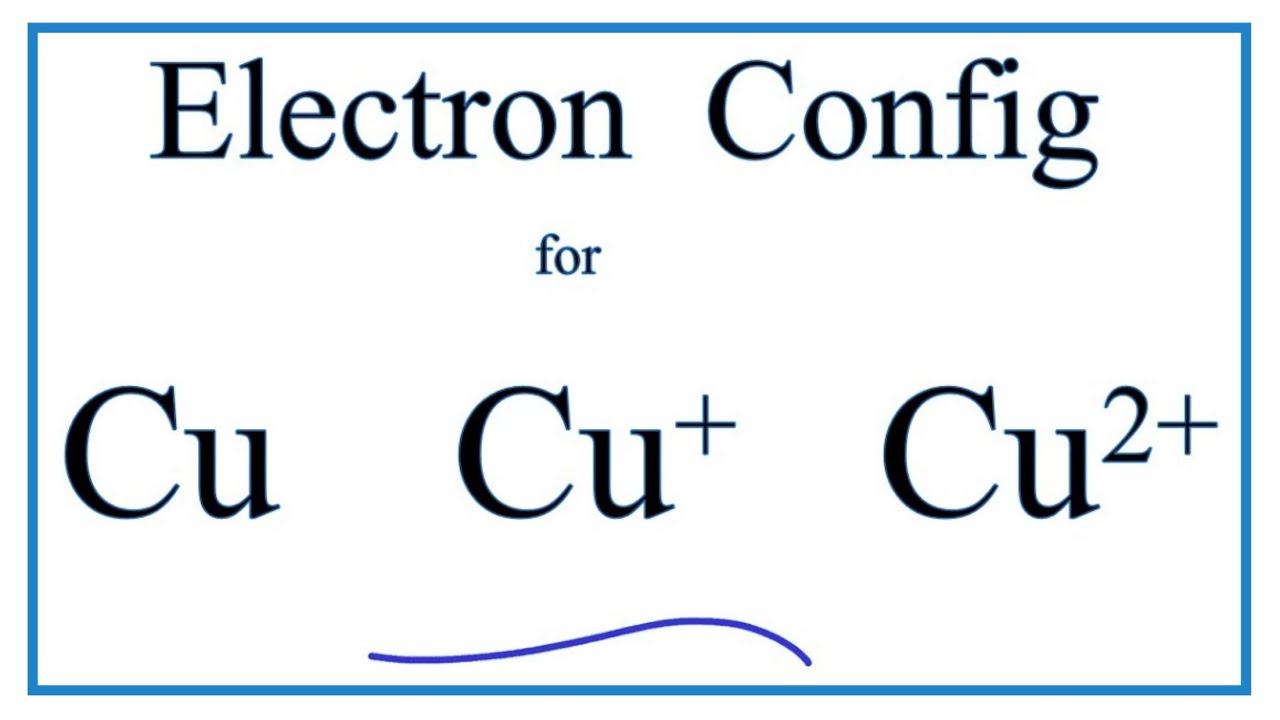
Electron Shell Configuration: | 1s2 |
2s2 2p6 | |
3s2 3p6 3d10 | |
4s1 |
Cu Atomic Number 29
For questions about this page, please contact Steve Gagnon.
